Kevetrin’s p53 modulation in ovarian cancer pati
Post# of 72451

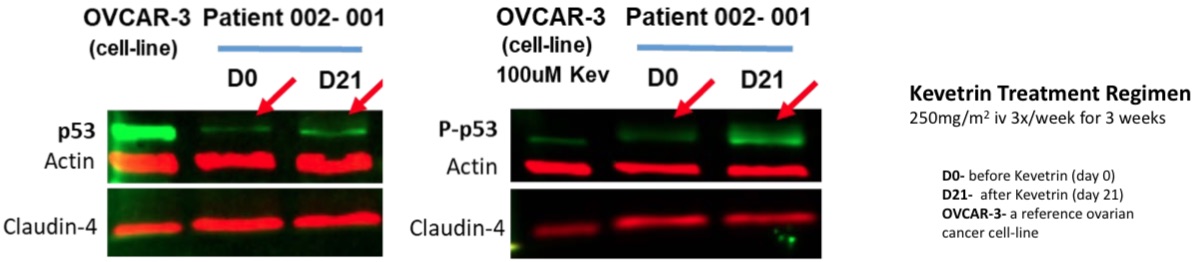
Quote:
Modulation of the p53 protein was observed in response to administration of Kevetrin. Pathways analyses also point to concomitant cell cycle modulation at the level of gene expression. Importantly, these data are the first to directly support, in ovarian cancer patient tumors, Kevetrin’s ability to affect p53 and associated molecular pathways—a central gene signaling network involved in regulating cell growth and the cell cycle, helping to prevent cancer.
In more detail, preliminary analyses used Western Blots to assess relative levels of key proteins extracted from tumor biopsies before and after a series of nine Kevetrin infusions administered over three weeks. The level of phospho-p53, the activated form of the protein, in addition to the noted p53 modulation, was also seen to change in response to Kevetrin administration. These findings confirm in patient tumors Kevetrin-induced anti-cancer effects similar to those demonstrated (pdf) preclinically in ovarian cancer cell-lines. These new data reinforce prior clinical data, from the earlier concluded Phase 1 study of Kevetrin in advanced solid tumors (see NCT01664000), in which observations of p21 expression in peripheral blood monocytes supported p53 involvement in Kevetrin’s mechanism of action.
http://www.ipharminc.com/press-release/2017/1...ncer-trial
 (2)
(2) (0)
(0)Innovation Pharmaceuticals Inc (IPIX) Stock Research Links
