My2centz, The paper you linked (thank you) sugg
Post# of 157019
The paper you linked (thank you) suggests a range of deaths from 9.06% to 15.65%.
Quote:
Findings In this cohort study of 38 517 adults who were admitted with COVID-19 to 955 US hospitals, rates of 30-day mortality or referral to hospice varied from 9.06% to 15.65% in the best- and worst-performing quintiles. In the early months of the pandemic, 94% of hospitals in a subset of 398 improved by at least 25%, and the strongest determinant of improvements in hospital-level outcome was a decline in community rates of infection.
Please find below the calculated p-values for such a scenario, we need to remember that weknow there were already 45 deaths in first half of trial.
Let’s assume near worst case scenario of 10% death rate. This will mean 19.5 (20) deaths for the 195 patients in second part of the CD-12 study for a total of 45+20=65 deaths in our CD12 trial.
Please find below the calculated p-values for such a scenario, we need to remember that we know there were already 45 deaths in first half of trial.
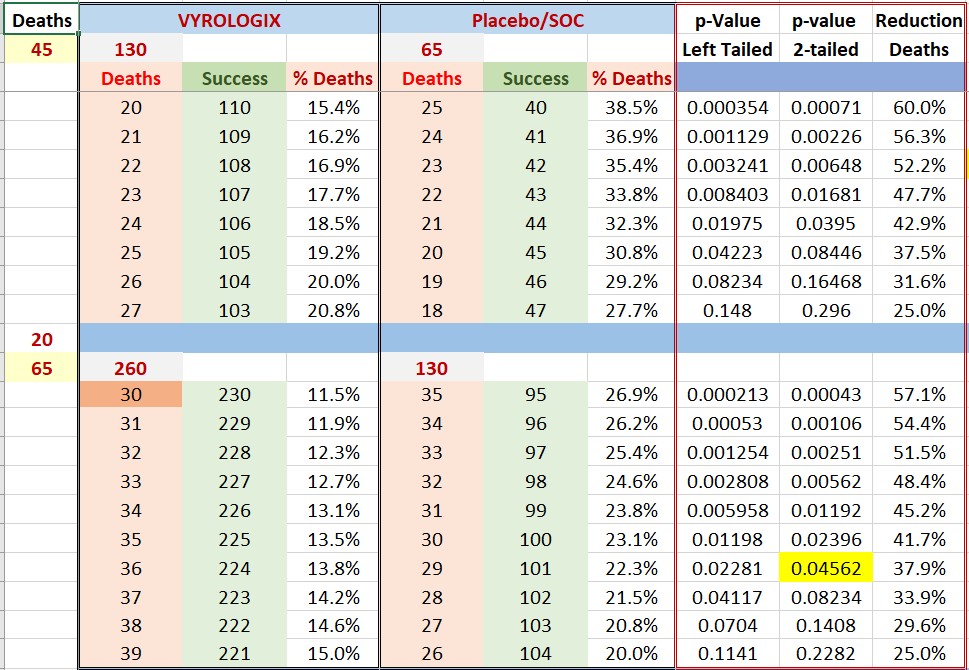
As you can see. An app. 40% reduction of deaths will bring us home. This is similar to what Mesoblast was aiming at (43% reduction). By the way, Mesoblast said that the improved care was responsible for the reduction of deaths and failure of their effort, from Mesoblast official release:
Quote:
The trial was powered to achieve a primary endpoint of 43% reduction in mortality at 30 days for treatment with remestemcel-L on top of maximal care in a trial of 300 patients. This projected mortality reduction was based on pilot data observed during the initial stages of the pandemic when control mortality rates were exceedingly high and prior to new evolving treatment regimens that have reduced disease mortality in ventilated patients.
Quote:
During the course of the trial, as the pandemic has evolved, numerous changes in the treatment regimens for COVID-19 patients occurred, including both prior to and while on mechanical ventilation that may have an effect on the mortality endpoint in the trial. These include extended management of patients prior to ventilator support, and use of experimental therapies such as dexamethasone, antivirals, and re-purposed immunomodulatory agents. All of these may have changed the natural course of ventilated patients and reduced overall mortality rates during the trial compared to the early stages of the pandemic.
 (5)
(5) (0)
(0)