Updated: Due Diligence on B-UP (thanks to F1ash fo
Post# of 72451

Trial Design
The primary objective of the P-o-C trial is to assess the frequency of clinical and endoscopic remission with Brilacidin administered per rectum in subjects with active UP or UPS after 6 weeks of treatment. Secondary objectives include evaluation of safety and tolerability of Brilacidin when administered per rectum, evaluation of clinical remission at Week 2 and Week 4, assessment of systemic exposure and/or pharmacokinetics of Brilacidin when administered per rectum, assessment of the efficiency of Brilacidin by biomarker evaluation of biopsy samples for interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1beta, and estimation of statistical power for subsequent trial(s) in UP and UPS.
The P-o-C trial will include 18 patients divided evenly into three cohorts. Cohort A is receiving 50 milligrams (mg) of Brilacidin once daily for 42 days. Dosing will be increased to 100mg and 200mg once daily for 42 days for Cohort B and Cohort C, respectively. Endoscopic evaluation of the rectum and mucosa up to 40 cm from the anal verge will be performed at screening and at the end of treatment/Day 42 (± 3 days). Per protocol, a safety committee will review safety and retention data (clinical laboratory findings, vital signs and adverse events) after 21 days of therapy for all six patients in each cohort before proceeding with initiating enrollment in the subsequent cohort.
http://cellceutix.com/cellceutix-receives-upd...xImnv.dpuf
First Patient Update
Cellceutix has been advised that the first patient in Cohort A remains on study. The clinical site administering Brilacidin to this patient has informed the Company, “Both the patient and the site staff have been amazed how the study drug works as all the symptoms decreased significantly within the 1st week of treatment .”
http://cellceutix.com/cellceutix-receives-upd...xImnv.dpuf
Interim Data
"A: Let me first touch on the ulcerative proctitis (UP) and oral mucositis (OM) trials. The UP trial is progressing smoothly and barring any unforeseen complications, we think that we will have some interim results sometime next quarter . This is a proof-of-concept study, which I believe can have a significant impact on the value of the Brilacidin franchise by serving as a gateway to other gastrointestinal diseases and conditions.”
http://seekingalpha.com/article/3988240-inter...olino#alt2
Ulcerative Proctitis
Abstract
Ulcerative proctitis is an idiopathic mucosal inflammatory disease involving only the rectum and is therefore an anatomically limited form of ulcerative colitis. Diagnosis is made based on clinical presentation, endoscopic appearance, and histopathology. Additionally, other etiologies of proctitis are excluded. The course of the disease is variable ranging from complete resolution to easily maintained remission to frequent relapses or refractory disease. Extension of inflammatory changes involving the proximal colon occurs in some cases. Rectal 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) or steroids are the initial treatments of choice with oral 5-ASA, sulfasalazine, or steroids used for treatment failures or patients unable to tolerate rectally administered drugs. Immunomodulators like azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine have been used successfully in small groups of patients who have not responded to 5-ASA or steroids. Oral or rectal 5-ASA products maintain remission but long-term steroid use should be avoided. Rare cases may require surgical therapy.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2780078/
Foam preparations for the treatment of ulcerative colitis
Abstract
Patients with ulcerative colitis uniformly have disease involving the distal colon. When patients have disease limited to the left colon or symptoms suggestive of active rectal inflammation, guidelines recommend topical rectal therapies as first-line agents either as monotherapy or in conjunction with oral products. Rectal delivery modalities offer the advantage of delivering high local concentrations of active medication to the site of maximal inflammation with minimization of systemic side effects. Methods of rectal administration include suppositories, liquid enemas and foams. Suppositories are limited to the treatment of rectal disease, and patients often have difficulty retaining the liquid enema secondary to its high volume and consistency. Rectal foams reliability extend to the descending and sigmoid colon with application. Foams are further characterized by increased viscosity, lower volumes, finer dispersion on the colonic mucosa, and increased adhesiveness to the colonic mucosa compared with liquid enemas. Additionally, rectal foam agents demonstrate equal efficacy to their liquid enema counterparts yet consistently yield better patient tolerance, lower incidence of side effects, and increased patient acceptability. Currently available agents include 5-aminosalicylic acid and corticosteroids, both first and newer generation. This review focuses on clinical trials assessing efficacy, tolerability, and patient preferences for these agents as well as describing the currently available rectal foam products.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21235478
Placebo Response Rate
Experience with foam preparations has demonstrated better retention and adherence, as well as more uniform distribution of medication in the distal colon and rectum, as compared with enemas and suppositories.
Analysis of the individual trials showed that 38.3% and 44% of patients in the budesonide arm achieved remission at 6 weeks as compared with 25.8% and 22.4% of the placebo groups (P=0.0324 and P<0.0001, respectively). Combined results showed a remission rate of 41.2% with budesonide foam and 24% with placebo (P<0.0001).
http://www.medpagetoday.com/meetingcoverage/acg/42311
Current and Future Therapies
Ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) are severe ailments affecting the digestive system.
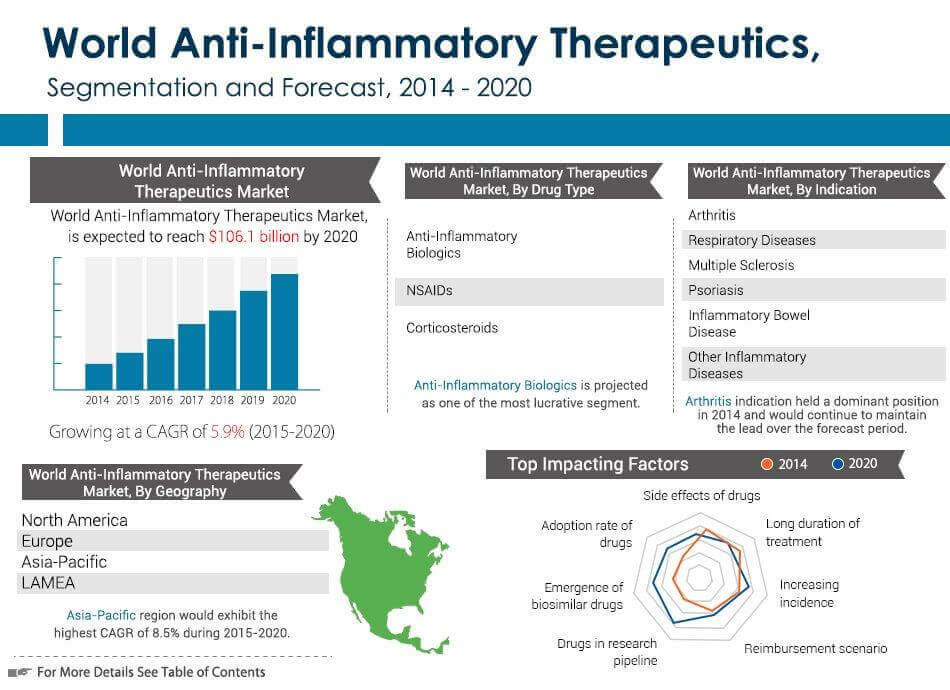
UC is a gastrointestinal (GI) disease that is localized to the large intestine, or colon, where inflammation can affect either the entire organ or a portion of it. Approximately 1.86 billion patients have been diagnosed with UC globally, with 1.54 billion patients currently receiving treatment. Traditional therapies have yielded $4.18 billion in annual sales around the world, a figure expected to increase to $6.85 billion by 2022 with the approval of various pipeline drugs.
CD can affect any part of the GI tract, but most commonly involves both the large and small intestines. Although CD is more severe than UC, the global prevalence is much lower, with only 1.3 million patients diagnosed and 0.8 million who currently receive treatment. Still, traditional therapies have resulted in an impressive $3.17 billion in global market sales, which is predicted to increase to $4.20 billion by 2022.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4123809/
Potential Market
The global ulcerative colitis (UC) market value will increase steadily over the coming years, growing from almost $4.2 billion in 2012 to approximately $6.6 billion by 2022, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.7%, according to a new report from research and consulting firm GlobalData.
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) has been continually dominating the UC market due to the success of Remicade. However, Remicade’s patent is set to expire between 2015 and 2018, which will knock J&J’s sales down from approximately $2 billion in 2012 to $1.5 billion by 2022, according to GlobalData.
Another key player in the UC industry, AbbVie’s Humira, will also lose its patent during the forecast period, with sales slipping from $1.2 billion in 2012 to $569 million by 2022.
https://healthcare.globaldata.com/media-cente...globaldata
http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/anti-...52061.html
 (5)
(5) (0)
(0)Innovation Pharmaceuticals Inc (IPIX) Stock Research Links
