 Most Americans have only a very limited understanding of how the Federal Reserve affects every aspect of our lives. Neither the Chairman of the Federal Reserve nor the twelve members of the Board of Governors are elected by the American public. The Federal Reserve operates independently in secret and has the power to make financial decisions that impact the financial well being of every American citizen.
Most Americans have only a very limited understanding of how the Federal Reserve affects every aspect of our lives. Neither the Chairman of the Federal Reserve nor the twelve members of the Board of Governors are elected by the American public. The Federal Reserve operates independently in secret and has the power to make financial decisions that impact the financial well being of every American citizen.
During the financial crisis of 2007-2008, Congress was shocked when they were asked to approve $700 billion in TARP funding to rescue the banking system. Little did Congress or the taxpayer know at the time, but $700 billion was actually small change compared to the $7.7 trillion that the Federal Reserve secretly committed itself to lend to the financial industry. The Fed only revealed the details of its massive secret loans when forced to by a Bloomberg freedom of information request.
Many economists believe that the actions taken by the Federal Reserve saved the United States from crashing into another Great Depression.
$7.77 trillion — The amount the Fed pledged to rescue the financial industry, according to Bloomberg research that examined announced, implied or actual upper limits on lending and guarantees. This number, which represents potential commitments, not money out the door, was first published in March 2009, when it peaked.
“One of the keys to understanding why we’ve avoided another Great Depression, so far, is to see how bold the Fed was in 2008 and 2009,” said Niall Ferguson, a Harvard University history professor. “That boldness consisted of a range of contingency commitments that backstopped the banking system. Just because they weren’t used doesn’t mean they weren’t important.”
Economic historians will be debating whether or not the Fed saved the American economy from a depression for decades, but now that the Fed has taken an active role in attempting to stimulate the economy and create jobs through quantitative easing (money printing), many analysts are starting to question whether the Fed will wind up destroying us while attempting to “save” us.
In an essay written by Dylan Grice of Societe Generale, serious questions are raised about the potentially adverse impact on America’s financial future due to the massive amount of currency debasement being caused by the Fed’s rampant money printing. The full article can be viewed at John Mauldin’s Outside the Box , a must read site.
At its most fundamental level, economic activity is no more than an exchange between strangers. It depends, therefore, on a degree of trust between strangers. Since money is the agent of exchange, it is the agent of trust. Debasing money therefore debases trust. History is replete with Great Disorders in which social cohesion has been undermined by currency debasements. The multi-decade credit inflation can now be seen to have had similarly corrosive effects. Yet central banks continue down the same route. The writing is on the wall. Further debasement of money will cause further debasement of society. I fear a Great Disorder.
I am more worried than I have ever been about the clouds gathering today (which may be the most wonderful contrary indicator you could hope for…). I hope they pass without breaking, but I fear the defining feature of coming decades will be a Great Disorder of the sort which has defined past epochs and scarred whole generations.
“Next to language, money is the most important medium through which modern societies communicate” writes Bernd Widdig in his masterful analysis of Germany’s inflation crisis “Culture and Inflation in Weimar Germany.” His may be an abstract observation, but it has the commendable merit of being true … all economic activity requires the cooperation of strangers and therefore, a degree of trust between cooperating strangers. Since money is the agent of such mutual trust, debasing money implies debasing the trust upon which social cohesion rests.
So I keep wondering to myself, do our money-printing central banks and their cheerleaders understand the full consequences of the monetary debasement they continue to engineer? Inflation of the CPI might be a consequence both seen and measurable. A broad inflation of asset prices might be a consequence seen, though not measurable. But what about the consequences that are unseen but unmeasurable – and are all the more destructive for it? I feel queasy about the enthusiasm with which our wise economists play games with something about which we have such a poor understanding.
If the authorities raise taxes explicitly and openly, voters know exactly why they have less spending power. They also know how much less spending power they have. But if the authorities instead raise money by simply printing it, they raise the revenue by stealth. No one knows upon whom the burden falls. People notice only that they can’t afford the things they used to be able to afford, or they can’t afford the things which everyone else can afford. They know that something is wrong, but they just don’t know what, why, or who is to blame. So inevitably they look for someone to blame.
So it is with monetary debasement, as Keynes understood deeply (so deeply, in fact, that it’s ironic so many of today’s crude Keynesians support QE so enthusiastically). In 1921 he said:
“By a continuing process of inflation, Governments can confiscate, secretly and unobserved, an important part of the wealth of their citizens. By this method they not only confiscate, but they confiscate arbitrarily ; and, while the process impoverishes many, it actually enriches some …. Those to whom the system brings windfalls …. become “profiteers” who are the object of the hatred … the process of wealth-getting degenerates into a gamble and a lottery .. Lenin was certainly right. There is no subtler, no surer means of overturning the existing basis of society than to debauch the currency. The process engages all the hidden forces of economic law on the side of destruction, and does it in a manner which not one man in a million is able to diagnose.”
History is replete with Great Disorders in which currency debasement has coincided with social infighting and scapegoating.
Which brings us to today. Despite the CPI inflation of the 1970s receding, our central banks have continued to play games with money. We’ve since lived through what might be the largest credit inflation in financial history, a credit hyperinflation. Where has it left us? Median US household incomes have been stagnant for the best part of twenty years (chart below)
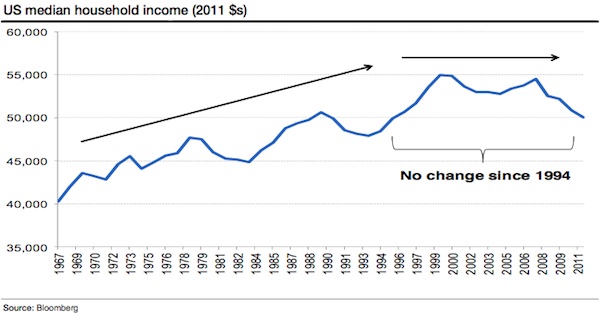
Yet inequality has surged. While a record number of Americans are on food stamps, the top 1% of income earners are taking a larger share of total income than since the peak of the 1920s credit inflation. Moreover, the growth in that share has coincided almost exactly with the more recent credit inflation.
These phenomena are inflation’s hallmarks. In the Keynes quote above, he alludes to the “artificial and iniquitous redistribution of wealth” inflation imposes on society without being specific. What actually happens is that artificially created money redistributes wealth towards those closest to it, to the detriment of those furthest away.
The Fed may have saved us from a depression only to wind up putting the vast majority of Americans into poverty worse than what a depression would have caused.


